
GCSE Periodic Table Explained 2025
The Periodic Table is one of the most important tools in chemistry, helping scientists and students understand the elements and their properties. Whether you are studying for your GCSE exams or just curious about how the elements are organized, this guide will help you break it down step by step.
How is the Periodic Table Organized?
1. Periods (Rows) and Groups (Columns)
- Periods (Horizontal Rows): The Periodic Table has 7 periods. Each period represents a new energy level of electrons in atoms. As you move from left to right across a period, the properties of elements gradually change.
- Groups (Vertical Columns): There are 18 groups. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of outer-shell electrons. Check GCSE Exam Dates 2025
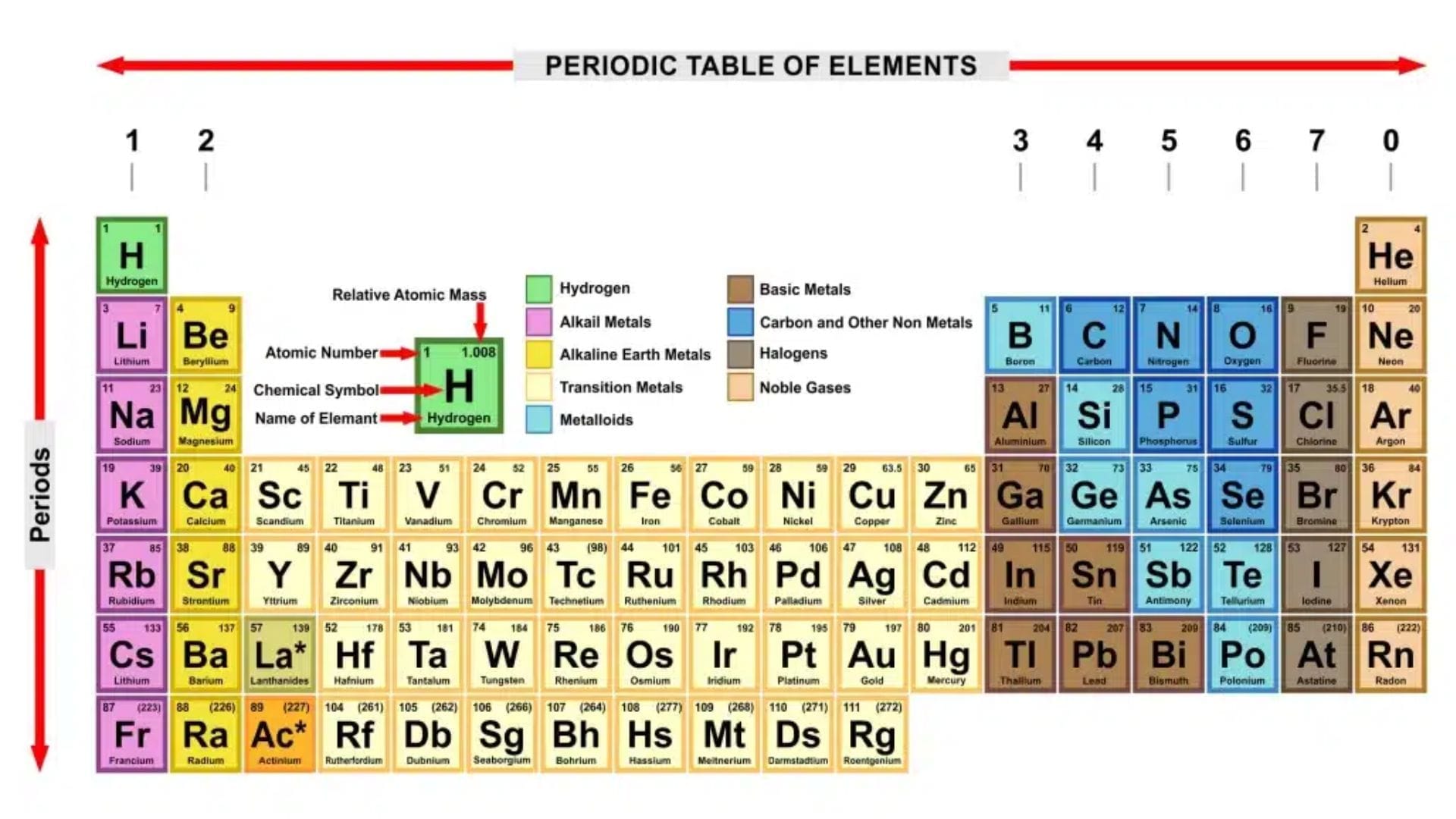
Main Element Groups in the Periodic Table
1. Group 1 – Alkali Metals
- Includes Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), etc.
- Very reactive, especially with water.
- Soft metals with low melting points.
2. Group 2 – Alkaline Earth Metals
- Includes Magnesium (Mg), Calcium (Ca), etc.
- Less reactive than Group 1 but still form basic (alkaline) solutions.
3. Group 7 – Halogens
- Includes Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), etc.
- Very reactive non-metals.
- Form salts when combined with metals (e.g., Sodium Chloride – NaCl).
4. Group 0 (or 8) – Noble Gases
- Includes Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), etc.
- Very unreactive due to their full outer electron shells.
- Used in lighting and balloons.
Metals vs. Non-Metals
- Metals (left side of the table) are good conductors of electricity and heat, malleable, and ductile.
- Non-Metals (right side of the table) are poor conductors and often brittle.
- Metalloids (stair-step lines between metals and non-metals) have properties of both.
Transition Metals (Middle of the Table)
- These include Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), etc.
- Hard, strong, and good conductors.
- Often used in construction and electronics.
The Importance of the Periodic Table in GCSE Chemistry
The Periodic Table helps students:
- Predict the properties of elements.
- Understand chemical reactions.
- Identify trends such as reactivity and electronegativity.
Knowing the layout and properties of the elements will make your GCSE Chemistry revision much easier!
Final Thoughts
The Periodic Table is a powerful tool in science, organizing elements in a way that helps us understand their behaviors and uses. Mastering its structure and trends will help you tackle GCSE Chemistry with confidence. Enrol for Online GCSE Courses
